[Could it be something about the ‘product’, maybe?]
Back in February this year, STT covered the unassailable fact that Australia’s Large-Scale Renewable Energy Target (LRET) – then set at a colossal 41,000 GWh – was completely unsustainable on every level – economic, political and social:
LRET “Stealth Tax” to Cost Australian Power Punters $30 BILLION
Our little analysis came at a time when a debate was underway about not whether, but by how much, the ultimate annual target needed to be cut to preserve a little of the wind industry’s furniture.
You see – with the ultimate target set at 41,000 GWh for 2020 – barely 16,000 GWh of power available from eligible renewable sources – and no new wind power capacity being built and none likely to be built – the imposition of the whopping $65 per MWh “shortfall charge” was then looming fast.
The actual cost to consumers of what is, pure and simple, a Federally mandated fine on electricity retailers – which will be recovered from all Australian power consumers – is around $93 per MWh, which is added to the average wholesale price of around $35 per MWh.
The Coalition’s wind industry front man, young Gregory Hunt calls it his “massive $93 per tonne carbon tax”. Its particular political toxicity was what focused the minds of our political betters in Canberra; and resulted in the first cut to the LRET’s ultimate annual target from 41,000 GWh to 33,000 GWh.
The principal logic that drove both the Coalition and Labor to slash the LRET target being fear of a power consumer (read “voter”) backlash – a revolt that will inevitably result when power consumers receive spiralling bills spelling out the fact that they are being hit with a mammoth, Federal electricity stealth tax.
Politicians of all hues know it – and, more importantly, Australia’s major electricity retailers know it: there is absolutely no way that – in an economy about to start going backwards – struggling businesses, manufacturing industries and cash-strapped households will tolerate the imposition of an enormous (and utterly pointless) Federal tax on electricity consumption.
Remember, this is the same electorate that smashed Julia Gillard over her ‘carbon tax’ – which, as another Federally mandated tax on electricity, was seen by voters as economically ‘toxic’; and gifted government to Tony Abbott’s Coalition 2 years ago.
After a lot of huffing and puffing – and shenanigans in the Senate – the reduced LRET target passed in June. At the time, the wind industry, its parasites and spruikers were howling one minute about the attack on “wonderful wind”; and breathing a collective sigh of relief that the dreaded “uncertainty” about the target was finally over.
Well, the trouble is that certain “certainties” still, and will always exist, in relation to the greatest economic and environmental fraud of all time: THESE THINGS DON’T WORK.
The retailers are about selling power on demand; not according to the vagaries of the wind.
Now, our favourite wind-worship cult-commanders – the Climate Spectator’s Tristan Edis (see this piece of wishful thinking) and ruin-economy’s Giles Parkinson – are furious about the fact that – despite the ‘agreement’ that settled on the latest LRET target – Australia’s retail power companies have absolutely NO interest in signing up to buy a “product” that can only ever be delivered at crazy random intervals, if at all. A product that brings total chaos for grid managers and allows peaking power operators to scoop up $millions in minutes:
The Wind Power Fraud (in pictures): Part 1 – the South Australian Wind Farm Fiasco
The Wind Power Fraud (in pictures): Part 2 – The Whole Eastern Grid Debacle
On top of that, the Senate Inquiry’s report (see our post here) into the great wind power fraud concluded that the adverse health effects caused by incessant turbine generated low-frequency noise and infrasound – such as sleep deprivation – are real; and not the product of some BIG COAL plot.
With 200 pages setting out the evidence of victims like SA turbine hosts, Clive and Trina Gare (see our post here), retailers are fully alive to the fact that it’s a matter of when, not if, wind farm neighbours start suing wind power outfits for $millions in damages. ‘Slam dunk’ common law claims in nuisance for the loss of the use of their homes; loss of property values etc, are brewing up as we speak. The outcome of which is that the $2 outfits used as fronts for the likes of Infigen will be insolvent, as soon as the victims file their claims:
Potential Wind Farm Neighbour Finds Idyllic Property is Now ‘Unsaleable’ at Any Price
Bankers, retailers and anyone else with real skin-in-the-game hate risk – of any description. Signing up to lend money to – or buy wind power from – an outfit liable to go under in heartbeat is bad enough, but where the wind power outfit in question is in the gun for $millions in liability claims for nuisance or negligence, then it’s RISK that only the crazy-brave would take on.
But it’s risk of a different kind that has poor old Giles Parkinson almost turning on the waterworks in this, his latest lament: Renewable investment drought to continue as utilities extend buyers’ strike
Giles cites Miles George – head of Australia’s most notorious wind power outfit, Infigen (aka Babcock and Brown) – as he rails against the fact that Australia’s 3 biggest retailers – Origin, EnergyAustralia and AGL – have no intention of entering power purchase agreements with wind power outfits, which means they will never obtain the finance needed to build any new wind power capacity, anywhere FULL STOP.
Although never one quick to join the dots, Giles fails to make the (fairly obvious) connection between the unwillingness of $billion outfits – like Origin – to contract with near-bankrupt Infigen – even though Giles focuses on Infigen’s latest whopping $304 million annual loss: ever heard of ‘due diligence’, Giles?
In the mother of all ironies, Infigen, again blames its latest financial disaster on ….. wait for it …. “PARTICULARLY POOR WIND CONDITIONS”.
Oh, mother!
But should Miles and the gang really be complaining? After all, the wind is – as they repeatedly tell us – “FREE”. Which calls to mind that old chestnut about “getting precisely what you pay for”.
We’ll pick up Infigen’s latest ‘be-calmed-cash-loss-calamity’ in another post, shortly.
The ONLY reason power retailers do any business with cowboys like Infigen and union backed thugs like Pacific Hydro, is to obtain renewable energy certificates (RECs); and, thereby, avoid the imposition of the shortfall penalty. However, the likes of Giles and Tristan are unable to recognise that power retailers do, in fact, have a ‘choice’, in that respect.
They do not need to purchase RECs at all – power retailers are perfectly entitled to pay the fine and collect it from their customers. Which brings us back to ‘pending political toxicity’.
The big retailers know full well that Australian power consumers will not tolerate being lumbered with fines that will add close to $22 billion to their power bills, over the life of the LRET scheme. Here’s the calculus of what no-one – on either side of government – is willing to reveal, let alone prepared to ‘sell’, to voters.
The LRET target is set by s40 of the Renewable Energy (Electricity) Act 2000 (here). At the present time, the total annual contribution to the LRET from eligible renewable energy generation sources is 16,000 GWh; and, because commercial retailers have not entered PPAs with wind power outfits for well over 2½ years – and have no apparent intention of doing so from hereon – that’s where the figure will remain.
In the table below, the “Shortfall in MWh (millions)” is based on the current, total contribution of 16,000,000 MWh, as against the current 33,000 GWh target, set out as the “Target in MWh (millions)”.
A REC is issued for every MWh of eligible renewable electricity dispatched to the grid; and a shortfall penalty applies to a retailer for every MWh that they fall short of the target – the target is meant to be met by retailers purchasing and surrendering RECs. As set out below, the shortfall charge kicks in this calendar year. Given the impact of the shortfall charge, and the tax treatment of RECs versus the shortfall charge, the full cost of the shortfall charge to retailers is $93. Using that figure, here is the cost of the shortfall penalty.
|
Year |
Target in MWh (millions) |
Shortfall in MWh (millions) |
Penalty on Shortfall @ $65 per MWh |
Minimum Retailers recover @ $93 |
|
2015 |
18.85 |
2.85 |
$185,250,000 |
$265,050,000 |
|
2016 |
21.431 |
5.431 |
$353,015,000 |
$505,083,000 |
|
2017 |
26.031 |
10.031 |
$652,015,000 |
$932,883,000 |
|
2018 |
28.637 |
12.637 |
$821,405,000 |
$1,175,241,000 |
|
2019 |
31.244 |
15.244 |
$990,860,000 |
$1,417,692,000 |
|
2020 |
33.85 |
17.85 |
$1,160,250,000 |
$1,660,050,000 |
|
2021 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2022 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2023 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2024 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2025 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2026 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2027 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2028 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2029 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
2030 |
33 |
17 |
$1,105,000,000 |
$1,581,000,000 |
|
Total |
490.043 |
234.043 |
$15,212,795,000 |
$21,765,999,000 |
The almost $22 billion in fines payable by power consumers will sit on top of the $22-23 billion worth of RECs that will also be added to power bills (see our post here).
Now, while Giles Parkinson’s article misses the point, his headline, which includes the words “buyers’ strike” touches on the “golden rule”: whoever has the gold, makes the rules.
When we first looked at this issue in February, we drew the analogy with another Federal government backed producer subsidy scheme, which also imploded due to a “buyers strike”.
With Giles, among others, struggling to come to terms with the “golden rule”, we think that it would be rude not to give that analysis another run.
In a little case of déjà vu, STT thinks that there are some significant parallels and important lessons to be learnt from how the Australian wool industry saw its Federally mandated subsidy scheme implode during the 1990s; all but killing the industry and costing growers and taxpayers tens of billions of dollars.
The wool industry’s “cause of death” was the Federally backed Reserve Price Support scheme (RPS), which set a guaranteed minimum price for all Australian wool.
A little background on the RPS
For over 150 years, Australia happily rode on the sheep’s back: until the 1970s the wool industry was, for the Australian economy, the “goose that laid the golden egg”; textile manufacturers from all over the world clamoured for the fibre; which was, for most of that time, the largest single commodity export by value; Australia produces over 80% of the world’s apparel wool. However, as fashions changed (the three-piece wool suit became, well, so “yesterday”) and new synthetics began to eat into its market share, the dominance of Australian apparel wool was no longer a certainty.
Against the backdrop of increasing competition, for the wool industry there was always the perennial issue, not only of fluctuating demand, but also of wildly fluctuating swings in production. Dorothea McKellar’s land of “droughts and flooding rains” meant that a few years of meagre production (and favourable, and even phenomenal, wool prices) would be soon eclipsed by sheds and wool stores overflowing with fibre ready for market (sending prices and woolgrower profits plummeting).
The response to these (often climate driven) marketing “swings and roundabouts”, was the establishment of the Australian Wool Corporation (AWC) and the RPS in 1973.
The RPS would set a minimum price for all types of wool, guaranteeing woolgrowers a minimum return; such that if supply exceeded demand, the AWC would purchase any wool being offered, if it failed to reach the minimum price set (referred to as the “floor price”).
Wool being offered at auction that failed to meet the floor price was purchased by the AWC and “stockpiled” (ie stored), until such time as either supply fell or demand conditions improved; at which point the AWC would offer stockpiled wool to the trade. The aim being the smooth and more orderly marketing of wool over the supply and demand cycle; with higher average returns to growers; and less risk for buyers and sellers along the way.
The scheme worked swimmingly (as designed and intended) until the late 1980s.
The reserve price set under the RPS was fixed in Australian dollar terms. However, with the float of the Australian dollar in 1983 (resulting in a massive 40% depreciation of the dollar between February 1985 and August 1986), maintaining the reserve price without reference to the terms of trade and fluctuations in trading currencies (particularly the US dollar) set the scheme up for a spectacular failure; simply because what goes down can just as easily go up.
During the 1980s, there was a solid increase in demand for wool, driven by demand from the USSR, a then fast growing Japan, buoyant Europeans, and a newly emergent China, as a textile manufacturer and consumer. However, that surge in demand occurred in the context of an Australian dollar trading in a range around US$0.55-75.
During the 1980s, under pressure from wool grower lobby groups, the floor price was continually increased: from 1986 to July 1988 the floor price jumped 71% to 870 cents per kilogram.
That did not, in itself, create any problems: a general surge in demand, relatively low production and a plummeting Australian dollar generated auction room sale prices well above the rising floor price, which reached their zenith in April 1988: the market indicator peaked at 1269 cents per kg, and the market continued its bull run for most of that year, well above the 870 floor price set in July.
However, as international economic conditions worsened, Australian interest rates soared (the consequence of Paul Keating’s “recession that we had to have”) and the value of the Australian dollar with it (hitting US$0.80 by early 1990), the market indicator headed south and, over the next few years, the AWC was forced to purchase over 80% of the Australian wool clip at the 870 cent per kg floor price. Adding to the AWC’s difficulties was a massive surge in production; driven by growers responding to the high and “guaranteed” floor price; and a run of exceptional growing seasons (1989 being a standout across Australia). Production went from 727 million kg in 1983/84 to over 1 billion kg in 1990/91.
Despite worsening market conditions, the AWC, under pressure from wool grower lobby groups, was forced to maintain the 870 cent per kilogram floor price.
However, from around August 1989, international wool buyers simply sat on their hands in auction sale rooms (in May 1990 the AWC bought 87.5% of the offering); and waited for the RPS to implode.
Knowing that the system was unsustainable, the last thing that buyers wanted was to be caught with wool purchased at prices above the floor price which, when the floor price was cut or collapsed, would immediately be worth less than what they had paid for it. Moreover, traders were dumping stock as fast as they could to avoid the risk of a collapse in the RPS and, therefore, a collapse in the price of any wool they happened to hold.
The RPS was ultimately backed by the Federal government. With the buying trade sitting on their hands, those responsible for maintaining the floor price ended up in a staring competition, the only question was, who would blink first: the AWC (or, rather, the government underwriting the RPS); or the buyers?
With the AWC purchasing millions of bales of wool at the floor price the cost of supporting the RPS was running into the billions of dollars: primarily the support came from a grower levy on sales, but, at the point which that soon became insufficient to support the RPS (despite upping the levy from 8% to 25%), support came from $billions in mounting government debt; the buyers had no reason to blink.
Instead, in May 1990, the government announced its decision to retreat to a new floor price of 700 cents per kilogram, and directed the AWC to fight on in support of the reduced floor price. The Minister for Primary Industry, John Kerin boldly asserting that the 700 cent floor price was “immutable, the floor price will not be reduced”.
But, having blinked once, the buyers largely continued to sit on their hands and simply waited for the government to blink again. The stockpile continued to balloon; and with it government debt: by February 1991 the stockpile reached 4.77 million bales (equivalent to a full year’s production); the accrued government debt stood at $2.8 billion; and the cost of storing the stockpile was over $1 million a day.
Faced with the inevitable, the government blinked, again: John Kerin was forced to eat his words about the floor price being “immutable”; on 11 February 1991, announcing the suspension of the floor price. The RPS had totally collapsed; the buyers had won.
The wool industry’s saga is beautifully, if tragically, told by Charles Massy in “Breaking the Sheep’s Back” (2011, UQP), which should be required reading for any of our political betters pretending to know more than the market (eg, the power market).
Which brings us to the lessons and parallels.
The LRET effectively sets the price for RECs: the minimum price is meant to be set by the shortfall charge of $65 per MWh (rising to $93 when account is given to the tax benefit), as the penalty begins to apply on the shortfall (as detailed above). That equation is based on an ultimate 33,000 GWh target.
In the event that the cost of the shortfall charge was reduced, there would be a commensurate fall in the REC price. Likewise, if the LRET target was further reduced: the total number of MWhs which would then attract the shortfall charge if RECs were not purchased would fall too; also resulting in a fall in the REC price.
In addition, any reduction in the LRET would simply result in a reduction in the demand for RECs overall: fewer RECs would need to be purchased and surrendered during the life of the LRET; again, resulting in a fall in the REC price. Of course, were the LRET to be scrapped in its entirety, RECs would become utterly worthless.
The retailers, are alive to all of this, hence their reluctance to enter PPAs for the purpose of purchasing RECs; agreements which run for a minimum of 15 years.
In December last year, Ian “Macca” Macfarlane and his youthful ward, Greg Hunt started running around pushing for a target of 27,000 GWh; and their boss made clear that he wanted to kill it outright. There followed overtures from the Labor opposition pitching for a target around 35,000 GWh.
Whether they knew it or not – with their public debate on what an amended target should be – in the staring competition with retailers – these boys blinked.
Faced with the inevitable political furore that will erupt when power consumers (ie, voters) realise they are being whacked with the full cost (and some) of the shortfall charge (being nothing more than a “stealth tax” to be recovered by retailers via their power bills), the pressure will mount on both sides of politics to slash the LRET – once again.
That both Labor and the Coalition have already blinked (in obvious recognition of the brewing political storm in power punter land over the inevitable imposition of the shortfall charge) is not lost on the likes of Grant King from Origin, and all of Australia’s other electricity retailers.
And for retail power buyers the choice of sticking with permanent recalcitrance has been made even easier: Tony Abbot making it plain that he would have cut the LRET even harder, were it not for a hostile Senate; and Labor’s Bill Shorten pushing for an entirely ludicrous 50% LRET – that would require a further 10,000 of these things to be speared all over Australia’s rural heartland. Where there was once ‘bipartisan’ support for these things, the major parties are diametrically opposed.

retailers blinking in the final LRET stare-off.
****
With the politics of the LRET already on the nose, like wool buyers sitting on their hands in sale rooms during 1990, waiting for the floor price to collapse, electricity retailers need only sit back and wait for the whole LRET scheme to implode.
Like wool buyers refusing to buy above the floor price and carry stock with the risk of the RPS collapsing, why would electricity retailers sign up for 15 year long PPAs with wind power outfits in order to purchase a stream of RECs over that period, knowing the value of those certificates depends entirely upon a scheme which is both economically and politically unsustainable?
However, the similarities between the wool market and the market for wind power end right about there.
There is, and always was, a natural market for Australian wool; the only issue during the late 80s and early 90s was the price that had to be paid by buyers to beat the floor price, set artificially under the RPS.
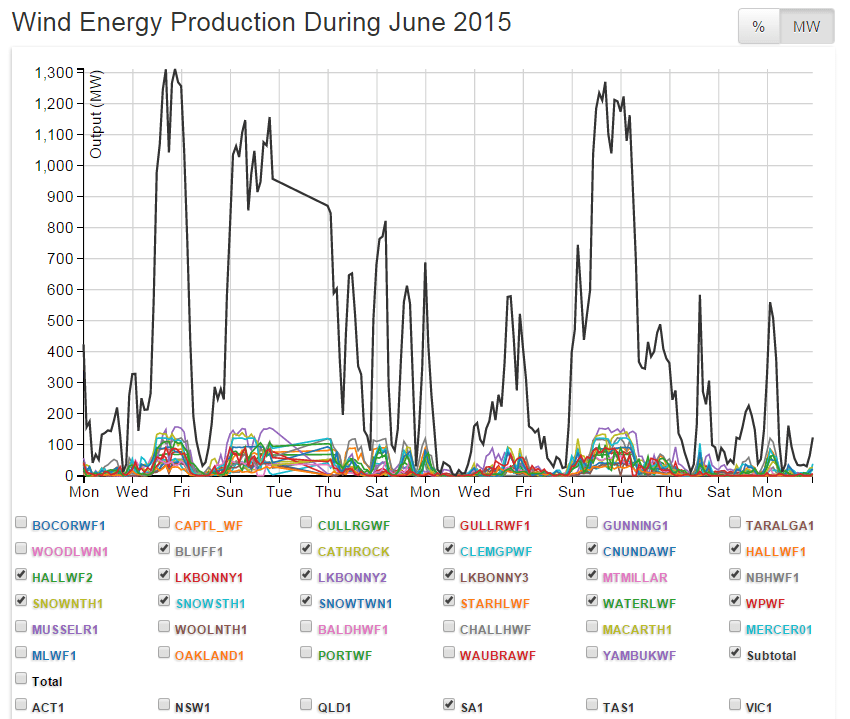
Wind power has no such market.
Available only in fits and spurts, and at crazy, random intervals, at a price which is 3-4 times that of conventional generation, retailers have no incentive to purchase it.
In the absence of the threat of the $65 per MWh fine (the stick), coupled with the promise of pocketing $93 as a subsidy in the form of a REC (the carrot), electricity retailers would not touch wind power with a barge pole: it simply has no commercial value.
Moreover, with an abundance of conventional generation capacity in Australia at present, retailers are very much in a “buyers’ market”. Overcapacity, coupled with shrinking demand (thanks to policies like the LRET that are killing mineral processors, manufacturing and industry) means that retailers can expect to see wholesale prices decline over the next few years, at least. And, for the first time in almost 20 years, a sharply declining Australian economy is a fast looming reality: unemployed households have an even tougher time paying rocketing power bills.
With those fundamentals in mind, electricity retailers will simply opt to pay the shortfall charge and recover it from power consumers, knowing that that situation will not last for very long.
Sooner or later, the Federal government (whichever side is in power) will have to face an electorate furious at the fact that their power bills have gone through the roof, as a result of a policy that achieved absolutely nothing.
Tony Abbott’s chances of leading his Coalition to a second term are tied to fundamental ‘mum and dad’ policies like electricity costs. Power prices matter; and in a battle between Australia’s Big 3 Retailers and the LRET, STT’s money is firmly on commercial self-interest.
STT hears that the big retailers are planning to wait until they look like exhausting the pile of RECs that they’re sitting on at present. At which point they’ll build some large-scale solar power facilities, in order to obtain the RECs needed to avoid the shortfall charge; for as long as it takes for the politics to turn gangrenous. As soon as the LRET gets scrapped, the plan is to sell the panels back into the residential roof-top market.
The cost of the LRET – and all that comes with it – to retail customers is at the heart of what’s driving retailers’ efforts to crush the LRET; and the wind industry with it.
This might sound obvious, if not a little silly: electricity retailers are NOT in the business of NOT selling power.
Adding a $45 billion electricity tax to retail power bills can only make power even less affordable to tens of thousands of households and struggling businesses, indeed whole industries, meaning fewer and fewer customers for retailers like Origin, AGL and EnergyAustralia.
The strategy adopted by retailers of refusing to ‘play ball’ by signing up for PPAs will, ultimately, kill the LRET; it’s a strategy aimed at being able to sell more power, at affordable prices, to more households and businesses.
And it’s working a treat, so far.
The wind industry’s incessant daily whining about “uncertainty”, is simply a signal that the retailers have already won. Once upon a time, the wind industry and its parasites used to cling to the idea that the RET “has bi-partisan support“, as a self-comforting mantra: but not anymore. And it’s the retailers’ refusal to sign PPAs that’s thrown the spanner in the wind industry’s works.
While the likes of Tristan, Giles and Miles will continue to work themselves into a lather about their inevitable fate, in the meantime, retailers, like Origin, AGL and EnergyAustralia, can simply sit back, watch the political fireworks, and wait for the inevitable and complete collapse of the LRET; and, with it, the Australian wind industry.


Ditto to the other comments . Jupiter wind seems determined to steamroll the community’s wishes and is still determined to lodge a DA later this year. I don’t understand why they are bothering as if ppa’s are hard to get nobody in their right mind would continue unless they were trying to onsell and who would buy? Is it somehow possible to gain finance without a ppa? STT is great in supporting all affected communities and is a wonderful resource but could it throw some light on this issue if possible. Perhaps I’m missing something. Regards , William.
Strange how Origin, AGL etc. non government backed companies, are not investing in these things by buying into power purchase agreements – yet the ACT Government which is funded from both its own and Federal taxes is investing in them.
Will they be asking for more money raised by taxes if things go wrong as a result of their power purchase agreements – if their partners in this scheme are unable to deliver the quantity of cut price energy they have agreed to?
After all it has to come from great distances, and there can be no guarantee that a) the energy they get will be from those places and b) that the wind will be blowing when the energy is needed.
Will they be increasing the price to their end customers when they cannot provide energy from these sites?
Will they just turn off the power switch when the power they are receiving is not coming from those sites, leaving customers – industrial, commercial and private with intermittent supplies?
Or will their customers have to pay a higher price at those times to be provided with energy from other sources – like backup gas, coal and hydro – or from other wind energy projects – if they happen to be producing at the time?
Will the operations of the Federal Parliament he affected by an intermittent energy supply or will they invest in their own power supply to prevent a chaotic energy supply situation.
If these big National and International investors are not willing to put money into these projects you have to wonder if the ACT Government is operating using a clear thought process or if they are infected from all the diatribe slop the wind industry ideologists produce.
Rational action cannot come soon enough to bring this industry down, and to restore a process of certainty of an ESSENTIAL Service being affordable to all.
An action which will bring back industry, business and investment into this wonderful country providing a worthy future for all.
The collapse can’t come fast enough. Thank you STT for all your efforts
As soon as gravity does it’s thing the better off we will be, and to hell with the windweasel grubs.